Table Of Contents
- What Is Production Planning Software?
- Production Planning vs. Scheduling vs. MRP/ERP
- Types Of Production Planning Software
- What Are The Key Features & Functional Modules?
- 1. Scheduling & Gantt Planning
- 2. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
- 3. Capacity & Resource Planning
- 4. Inventory & Supply Visibility
- 5. Integration & APIs
- Analytics & What-If Simulation
- What Are The Benefits Across Business Sizes?
- 1. Small & Medium Manufacturers
- 2. Large & Complex Operations
- How to Choose The Right Software?
- 1. Business Needs & Complexity
- 2. Budget & Pricing Models
- 3. Technical Fit & Integrations
- 4. Implementation Time & Support
- 5. Scalability & Future-Proofing
- Feature Checklist
- Comparison Use Cases & Examples
- 1. Best For Small To Medium-Sized Businesses: Katana
- 2. Best Budget Software: MrPeasy
- 3. Best For Large Businesses And Multi-Site Operations: Infor Or ToolsGroup
- Implementation Best Practices
- 1. Phased Deployment
- 2. Training And Change Management
- 3. KPI Setup
- Expert Tips & ROI Metrics
- Key Performance Indicators To Monitor Success
- Projected ROI Timeline
Production Planning Software: Complete Guide, Features, Benefits & Best Solutions For Modern Manufacturing
It demands smart coordination. This is where production planning software becomes essential. This digital tool serves as the brain of a factory.
It further helps businesses schedule tasks, manage materials, and track every stage. These digital tools serve as the brain of a factory.
It replaces slow, manual spreadsheets with accurate and data-driven plans by automating complex calculations.
A well-constructed plan is the foundation of business success. According to NetSuite, effective production planning allows manufacturers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and meet customer demands on time.
Without these tools, the companies often face costly delays and inventory errors.
The industry is growing rapidly! The experts predict that the market for this software will grow at a CAGR of 7.33% through 2033, driven primarily by the rise of AI and other smart factory technologies.
In this guide, you will learn:
- The core features of the modern production planning tools.
- How the software improves its efficiency and lowers costs.
- Lastly, the tip for choosing the right system for your business.
What Is Production Planning Software?
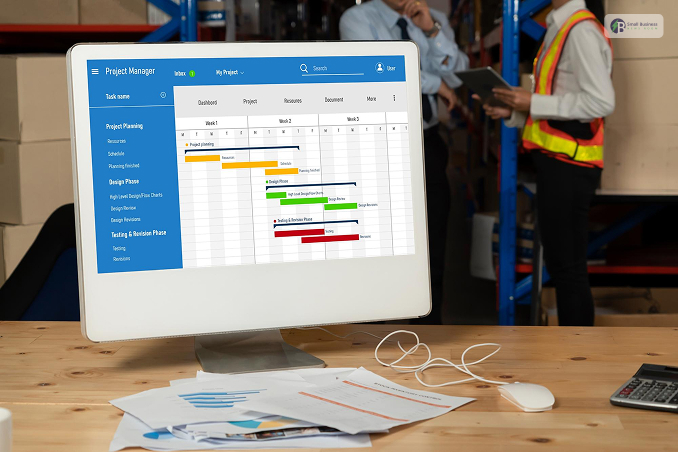
Production planning software is a digital solution that helps manufacturers design and manage their production journey!
Instead of using messy paper notes, this tool can easily centralise everything in one place. Moreover, it covers four main areas:
- Planning: Deciding what to make and when!
- Scheduling: Setting exact times for specific machines and workers.
- Resource allocation: Assigning progress as it happens on the factory floor.
- Real-time visibility: Tracking progress as it happens on the factory floor.
If you can compare them to the manual methods, such as simple spreadsheets, this software is much more powerful.
While Microsoft Excel is easy to use, it often leads to human errors and outdated data.
Modern software updates automatically. It ensures everyone sees the same information instantly.
Production Planning vs. Scheduling vs. MRP/ERP
It is easy to continue these terms, but they serve different roles in a factory:
- Production planning: it focuses on the big-picture strategy and overall goals.
- Production scheduling: This focuses especially on the daily details, such as which worker is on machine A at 9 M.
- MRP (Material Requirements Planning): A specific tool that focuses on managing raw materials and inventory.
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): A massive system that connects everything, including finance, HR, and sales.
Types Of Production Planning Software
There are three main ways companies use these tools:
- Stand-alone tools: This is specialised applications that handle planning only. These are often faster to set up, but do not always communicate with other departments.
- ERP Integrated Modules: This has planning features that are built directly into a larger ERP system. This keeps all company data in one database.
- Cloud vs. On-Premise: Cloud software is hosted online and accessible anywhere, making it great for scaling.
On-premise software is installed on local servers, giving you more control but requiring more IT maintenance.
What Are The Key Features & Functional Modules?
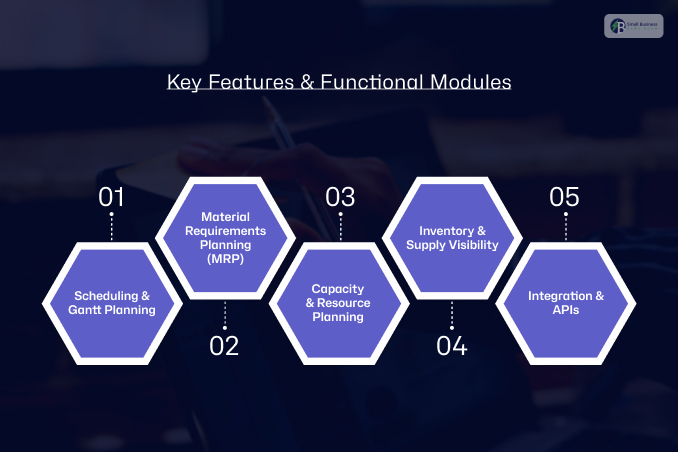
When you’re selecting production planning software, you want software that makes life easier.
Moreover, good software should be a single source of truth for your factory. Here are the must-haves and how they work.
1. Scheduling & Gantt Planning
The heart of a productive shop floor is visualization. Most modern software has a Gantt chart with drag-and-drop functionality.
How it works: You put all your production orders on a timeline. If a machine goes down, you can reschedule a task to another time or machine.
Why it’s great: It takes care of dependencies. If step one is late, step two starts late too.
2. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
This functionality ensures you never run out of screws, fabric, and parts. It uses your Bill of Materials (BOM), a list of every part in a product, to forecast what you need.
Example: The NetSuite MRP module calculates exactly how much wood and glue you need based on your current stock and the number of chairs you need to make.
3. Capacity & Resource Planning
This tool prevents overworking your team or your machines. The software understands machine and human capacity.
How it works: It understands that Machine A can only work 8 hours a day. If you schedule 10 hours, it will alert you immediately.
4. Inventory & Supply Visibility
Good software can often synchronize your inventory levels in real-time. It matches your current inventory with future needs.
How it benefits you: You can view committed inventory versus available inventory, ensuring that you do not sell the same product twice.
5. Integration & APIs
Your planning software should integrate with other software. It must communicate with them via APIs.
The most important integrations: Integrate your planner with QuickBooks for accounting or Shopify to view new orders as they occur.
Analytics & What-If Simulation
This allows you to run “what-if” scenarios without altering your actual schedule. Example: You can simulate how delivery dates would change if a major supplier is two weeks late.
Related Resource: 15 Best Inventory Management Software for Small Businesses
What Are The Benefits Across Business Sizes?
Implementing production planning software can provide you with a massive competitive edge. It significantly boosts the efficiency.
This way, you can ensure that machines never really sit idle and the workers always know their next task.
Second, it can help you ensure waste reduction. When you exactly know how much material a job requires, you kind of stop over-ordering.
Moreover, this leads to better forecast accuracy, allowing you to predict future needs based on past trends.
As a result, you see reduced lead times and much higher delivery reliability. Customers stay happy because they receive orders exactly when promised.
1. Small & Medium Manufacturers
For smaller shops, the biggest advantage is the lower entry barrier. In the past, advanced tech was too expensive.
Now, cloud-based SaaS tools allow small businesses to access professional features for a monthly fee.
These systems are easy to set up and do not require a large IT team. This flexibility helps small teams scale without huge upfront costs.
2. Large & Complex Operations
Large enterprises face deeper challenges. They need advanced features such as finite capacity planning.
This accounts for real-world constraints, such as machine maintenance or power outages. You can also find that many large firms use Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS).
These systems use complex math to solve global supply chain puzzles instantly. The shift toward digital tools is accelerating.
According to Deloitte, 83% of manufacturers believe smart factory solutions will transform the way products are made over the next five years.
How to Choose The Right Software?

The selection of the appropriate production planning software requires a proper plan. This decision tree will help you choose what suits you.
1. Business Needs & Complexity
Begin with your production capacity. If you produce many simple products, you require speed.
If your product line is complex with multiple components, you require detailed information.
Organize a structure, such as the Software Selection Methodology, to outline your specific needs before browsing through demos.
2. Budget & Pricing Models
Now, consider your budget. Most contemporary software follows a SaaS (Software as a Service) pricing structure with monthly charges.
This is more financially favorable than purchasing expensive perpetual licenses. Always compare the price with the value of your saved time and reduced waste.
3. Technical Fit & Integrations
Your new software should integrate with your existing software.
Ensure it integrates well with your accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks) or e-commerce platform (e.g., Shopify).
If it doesn’t integrate well, you’ll spend time manually entering data.
4. Implementation Time & Support
How soon can you start using it? Some software takes weeks, while others take months.
Ensure you select vendors who provide quality training materials and Service Level Agreements (SLAs). This will help you quickly access support if your software goes down.
5. Scalability & Future-Proofing
Finally, consider your future plans. Your software should scale with you.
Ensure your software is compatible with AI and predictive analytics to remain competitive as technology advances.
Feature Checklist
Before you sign the contract, ensure you check the following:
- Deployment time: Can you go live in under 90 days?
- API readiness: Does it have open APIs for custom integration?
- User license limit: Are there additional costs as your team grows?
- Mobile access: Can your managers view the schedule from their mobile device?
Comparison Use Cases & Examples
The selection of production planning software is based on your goals. Each software has its strengths, depending on your business size and level of complexity.
1. Best For Small To Medium-Sized Businesses: Katana
Katana is best suited for small- to medium-sized manufacturers seeking a more visual experience.
This software provides real-time visualization of the shop floor and plans activities at a detailed level.
Best feature: The software has an automatic booking engine that assigns products to the most urgent orders.
Cost: Mid-range SaaS pricing that is suitable for small to medium-sized businesses.
2. Best Budget Software: MrPeasy
MRPeasy is the best software for people who are looking for software with great features at a low price. This software provides planning and procurement in one easy-to-use interface.
Best feature: The software provides accurate cost and lead time calculations based on your current production speed.
Cost: This software is known for its clear and affordable pricing plans for small businesses.
3. Best For Large Businesses And Multi-Site Operations: Infor Or ToolsGroup
Large businesses require enterprise-level planning software that can meet their complex needs. These software solutions provide advanced supply chain management for multiple factory sites.
Best feature: The software uses AI to predict demand changes and adjust production schedules across multiple sites simultaneously.
Cost: High-end enterprise pricing suitable for the business’s size and needs.
Implementation Best Practices
Rolling out your production planning software requires careful planning. Even the best software will not work if it is not implemented correctly from the beginning.
Data Cleanup and BOM Verification begin with clean data. Thus, you must review your Bill of Materials (BOM) to ensure all parts and quantities are correct.
If your master data is incorrect, the software will produce erroneous schedules. As the old saying goes, “garbage in, garbage out.”
As a result, you must utilize tools such as the NetSuite Data Migration Guide to clean up your records before importing.
1. Phased Deployment
Don’t attempt to fix everything at once. Phase your deployment. Begin with basic production planning functionality first.
Once your staff are comfortable, introduce complex functionality such as shop-floor tracking or automated procurement.
2. Training And Change Management
Software is only valuable if your staff uses it. Build a positive atmosphere with hands-on training sessions.
Find “power users” to assist other staff members. Effective change management minimizes resistance and accelerates adoption.
3. KPI Setup
Lastly, measure your success. Monitor key performance indicators to determine if the software is effective. Monitor:
- Schedule Adherence: Are you completing jobs on schedule?
- Throughput: How many units are produced per shift?
- WIP Aging: How long do items remain as “Work in Progress”?
Expert Tips & ROI Metrics
To maximize your production planning software in 2026, follow these top tips:
- Planning Cycle: Establish a regular review cycle. Most top companies today employ “Agentic AI” to simulate rollouts and forecast issues before they occur.
- Collaborative Planning: Overcome departmental barriers by engaging finance, sales, and production teams early on.
- Safety Stock Calculations: Employ data models that factor in lead-time adjustments and weather patterns to calculate additional stock. This serves as a safeguard against unexpected supply chain disruptions.
Key Performance Indicators To Monitor Success
Monitor these important metrics to ensure your software delivers tangible benefits:
- Schedule Compliance: Check if you complete projects on schedule. Strive for high compliance rates to prevent aged work-in-progress (WIP).
- On-Time Delivery (OTD) Rates: In 2026, a best-in-class OTD rate is 95% or better. Companies with optimized systems can improve OTD from 78% to 93% in 8 months or less.
- Inventory Turns: Target a ratio of 5 to 10 for most manufacturing industries. This indicates you are selling and replenishing inventory effectively without holding idle inventory.
Projected ROI Timeline
The return on investment (ROI) for production planning software occurs sooner in 2026:
- SMBs: Small to mid-sized businesses typically realize ROI in 4-8 months. Quick wins, such as shop-floor analytics, can be deployed in 30 days.
Enterprises: Large companies typically target ROI in 1-3 years. Companies leveraging AI-based optimization can realize significant benefits in 90 days or less.















